Because of their wide application, all-season tires are an important segment in the overall tire market. Compared to winter and summer tires, all-season tires dominate market share in the leading North American and Chinese tire markets. Also relevant are winter tires that, because of increasing regulation, are becoming a driver of replacement tire sales.
These and other important trends are detailed in the new “All-Season vs. Winter Tires to 2024: A State-of-the-Art Report,” from Smithers. The report assesses the key technologies, materials and market drivers that enable tire performance in these two critical product segments, including regulatory, end-use (passenger cars and light trucks) and regional outlooks. It reviews these factors from a global perspective and from the perspective of the main tire-consuming regions for all-season and winter tires.
Due to the large temperate climate regions of both the U.S. and China, all-season tires are considered the standard for most of the U.S. states and Chinese provinces, except for the very northern tier regions. Even in many of the northern regions, and in parts of southern Canada, all-season tires have a high market share, and season-specific tires have decreased importance. This is in contrast to regulatory requirements in Europe and in the more severe winter weather provinces in Canada, where laws (as in Quebec and, most recently, British Columbia) or incentives in other Canadian provinces have led to the market division between summer and winter tires.
Regulatory Environment
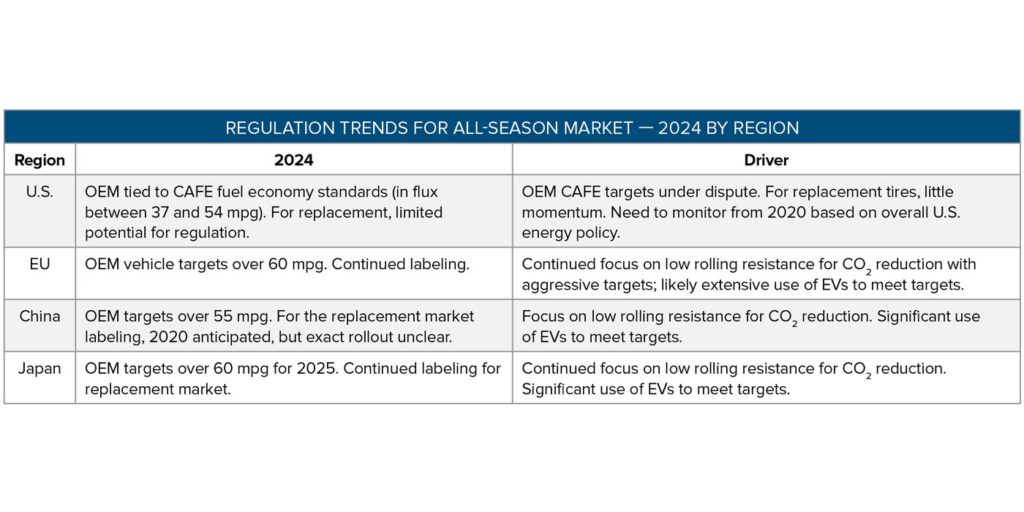
The most important regulatory driver for all-season tires is the OEM vehicle fuel economy standards. Fuel economy standards are increasing for vehicle OEMs in the EU, Japan, China and North America. Targets for the EU and Japan in the 2025 timeframe are rising to over 60 mpg. Originally, U.S. CAFE standards were scheduled to increase to 54.5 mpg in 2025 for passenger cars and 47 mpg as a fleet average, but the standards have been revised downward to 44 mpg and 47 mpg, respectively.
The U.S. vehicle market is continuing to move dramatically toward fewer fuel-efficient SUVs/light trucks, which now make up 55% of light-duty vehicle sales, and the U.S. still has fuel economy improvements to make to reach even lower fuel economy targets. Because tires contribute directly to vehicle fuel economy, automakers will prioritize low-rolling resistance all-season tires in the U.S. for fuel economy gains. In other regions, higher fuel economy standards will increase the drive toward super low-rolling resistance tires.
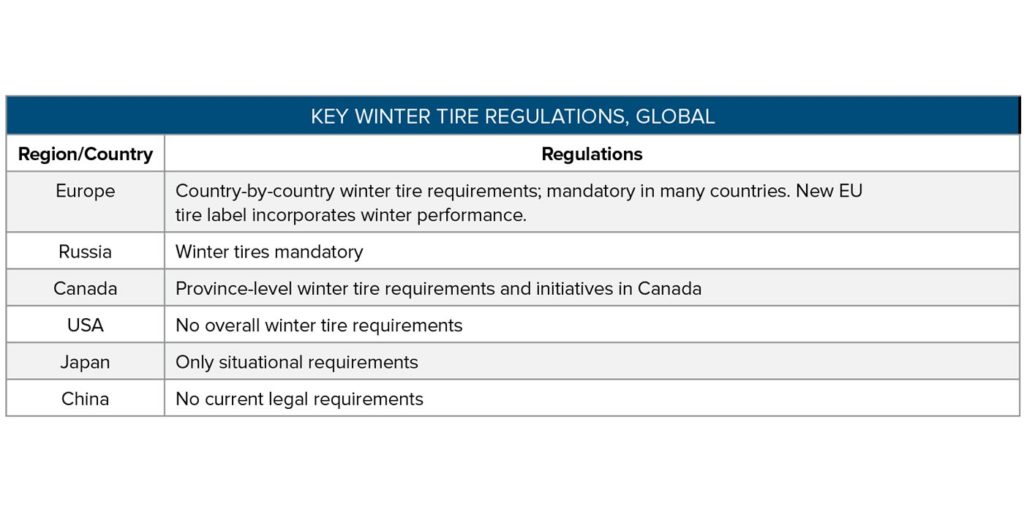
For winter replacement tires, regulation is a major driver of sales. Europe leads in winter tire regulation, with Germany’s winter tire mandate leading the way. Other EU countries have their own regulations, but because travel among countries is prolific, most consumers use winter tires. In North America, the U.S. does not have a winter tire regulation, and demand for winter tires is concentrated in the northern states. Only in Quebec, Canada, are strict winter tire requirements mandated.
In Asia, Japan’s winter liability laws have encouraged extensive winter tire adoption, while no regulation exists in China. Winter tires are designated by the Alpine snowflake 3MPSF (three-peak mountain snowflake) and M+S designations. Winter tire performance is segmented between Nordic/high snow and ice conditions and more moderate Central European winter conditions.
All-weather tires are a new market development gaining interest in Europe; they also have recently been introduced in North America. They offer winter tire labeling with the Alpine snowflake, signifying a three-peak mountain snowflake rating, along with year-round performance. Market potential exists to expand the all-weather/four-season tire category in south Central Europe, the northern U.S., Japan and, eventually, China.
Climate Changes
Climate patterns over the past 50 years have shown increasing temperatures. This is especially important for the future of winter tires and, to some extent, all-season tires. Increasing temperatures have been significant in northern climates, such as the northern U.S., where the average temperature has increased over 5° Fahrenheit, putting more cities in moderate winter vs. severe winter climates. The temperature change has generally led to decreases in snowfall and increases in rain; these trends are projected to accelerate over time.
The overall long-term trends mean winter tires will need to focus more on wet grip and grip on black ice films. In addition, winter tires will need to have wet snow performance in freezing conditions, instead of classic Nordic winter tire conditions: heavy and dry snow with thick ice conditions at temperatures significantly below freezing.
Sustainability Initiatives
Coinciding with climate trends, sustainability has become an important factor for consumers and tire manufacturers. Major tiremakers are adopting corporate social responsibility policies emphasizing sustainability, including the use of renewable materials, especially those that are bio-based.
Leading tire companies have committed to sustainability goals. They are not only identifying actions and developing consumer branding around these initiatives but also are accelerating the development and commercialization of sustainable materials, which provides a performance benefit as a compound formulation component.














