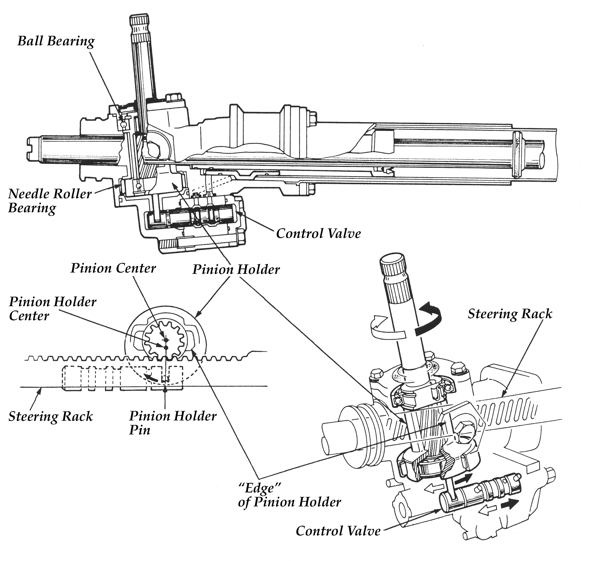
 Variable-assist, variable-rate or variable-effort power steering is used on a growing number of vehicles. Variable assist is a way of providing the best of both worlds: finger-tip parking maneuverability at low speed, and reduced assist at higher speeds for greater stability and road feel.
Variable-assist, variable-rate or variable-effort power steering is used on a growing number of vehicles. Variable assist is a way of providing the best of both worlds: finger-tip parking maneuverability at low speed, and reduced assist at higher speeds for greater stability and road feel.
As a vehicle’s speed increases, less effort and assist are needed to steer the wheels. Variable-rate steering, by comparison, applies more assist at low speed when it is needed most and reduces assist at higher speeds when it is needed least.
Diagnosis
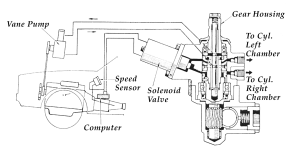
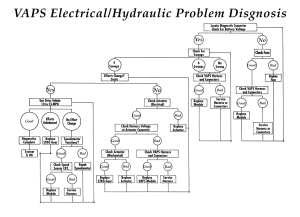 Problems with electronic variable-assist systems include all of the same things that can go wrong with a conventional power steering system (leaks, center wear in the steering gears, pump and hose failures, etc.), plus problems with the control electronics including the vehicle speed sensor circuit, the solenoid valve and control module. Accurate diagnosis, therefore, is essential to minimize returns and/or comebacks. Most of these systems provide diagnostic fault codes that can be accessed with a voltmeter, test light or scan tool to pinpoint the nature of the fault (if the fault is electronic rather than mechanical or hydraulic).
Problems with electronic variable-assist systems include all of the same things that can go wrong with a conventional power steering system (leaks, center wear in the steering gears, pump and hose failures, etc.), plus problems with the control electronics including the vehicle speed sensor circuit, the solenoid valve and control module. Accurate diagnosis, therefore, is essential to minimize returns and/or comebacks. Most of these systems provide diagnostic fault codes that can be accessed with a voltmeter, test light or scan tool to pinpoint the nature of the fault (if the fault is electronic rather than mechanical or hydraulic).
If power to the solenoid or control-valve actuator is lost, the valve keeps the bypass circuit closed so full power assist is provided under all driving conditions. The only indication of trouble, therefore, might be a loss of road feel and/or increased steering sensitivity at highway speeds.
It’s important to remember that variable-rate power steering only reduces the amount of pressure that reaches the steering gear at higher road speeds. The only way it could reduce power assist at low speed would be in the unlikely event the actuator or solenoid valve failed in the open position. This could cause a noticeable reduction or loss of power assist.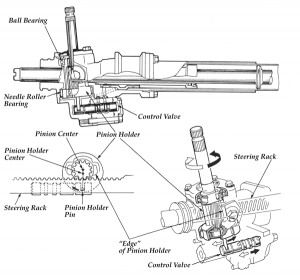
If the control solenoid fails on a Ford EVO system, or the control circuit for the solenoid is lost, the valve is designed to keep the bypass circuit closed so full power assist is provided under all driving conditions. The only indication of trouble would be a loss of road feel and/or increased steering sensitivity at highway speeds. However, if the EVO solenoid valve jams in the open position, there would be little or no power assist at any speed.
On GM’s Magnasteer racks, loss of current to the magnetic coils would cause a loss of power assist at low speed. Coil resistance can be checked with an ohmmeter, and should read about two ohms. An infinite (open) reading indicates a bad coil (requires replacing the rack since the coils are not serviceable). Checking for shorts between both sides of the coil assembly and rack housing is also recommended.
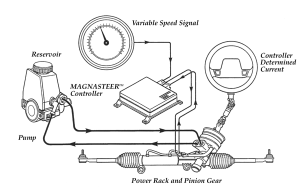 The system does have self-diagnostic capability, but there is only one fault code: C1241 (Magnasteer circuit malfunction). The code is set if the module detects an open or a short in the coil circuit. If this code is present, the Magnasteer system is disabled and will not vary the steering effort as vehicle speed changes. The C1241 body code can be read with a Tech 2 or equivalent scan tool. The Tech 2 tool can also be used to perform a Magnasteer function test. The test varies the current to the coil so you can check for a change in steering effort when turning the steering wheel.
The system does have self-diagnostic capability, but there is only one fault code: C1241 (Magnasteer circuit malfunction). The code is set if the module detects an open or a short in the coil circuit. If this code is present, the Magnasteer system is disabled and will not vary the steering effort as vehicle speed changes. The C1241 body code can be read with a Tech 2 or equivalent scan tool. The Tech 2 tool can also be used to perform a Magnasteer function test. The test varies the current to the coil so you can check for a change in steering effort when turning the steering wheel.
Replacement racks for variable-assist power steering applications are available with or without an EVO control solenoid. As long as the original EVO control solenoid is working OK, it can be removed and installed on the replacement rack to save your customer a few bucks. There’s no need to replace the whole rack if only the EVO solenoid valve is defective.
On GM Magnasteer applications, the whole rack must be replaced if the rack or control unit is defective because the Magnasteer unit is part of the rack. Handle with care because the permanent magnets inside the Magnasteer valve assembly and connector are fragile and can be easily damaged.